Paper 8: Culture Studies
Topic:
◙ Five Type of Culture Studies
Name: Sagar G.Ladhva
Roll No: 25
Semester : M.A. -2
Enrollment No: 14101022
Email.id: sagarladhva5507@gmail.com
Submitted To:
Smt.S.B.Gardi
Department
of English
M.K.B.U.
- Bhavanagr Universtity
Overview of Culture
Studies:
Culture:first
when study this topic culture then arising many questions like that: What is
Culture? How the Culture Main role of social & literature in study? Is this
study believing of only philosophy of Culture or not only social culture study
including them? So let’s we start in culture study importance and what main
purpose of culture studies.
Culture is derived from Latin the
word Culture
and ‘Colere’ and to honor and protect. Culture is a system of
knowledge. Some critics are defined the culture like:
“Culture is a march towards
perfection” - Mathew Arnold
“Culture is everything you don’t have to
do’’ -
Brain Eno
“Culture study is the study of lively
culture’’ - Raymond
Williams
Culture: “The
deposit of knowledge, experience, beliefs, values, attitudes, meanings,
hierarchies, religion, notions of time, roles, spatial relations, concepts of
the universe, and material objects and possessions acquired by a group of
people in the course of generations through individual and group striving'' - Samovar & Porter
The
Origin of Cultural Study: Started on 1964 – Richard Hoggart.
It
derives from the CCCS (Center for Contemporary Cultural Study) at the Univ. of
Birmingham established in 1964.he
founding fathers are:Richard
Hoggart, Raymond Williams, E.P. Thompson, Stuart Hall.They
concern with the changing of English cultural life.
Some Structural
Definition:
“A
historically transmitted pattern of meaning embodied in symbols, a system of
inherited conceptions expressed in symbolic forms” – Geertz (was an American
anthropologist)
“The term culture
usually is reserved to refer to the systems of knowledge used by relatively
large numbers of people” [i.e., national groups] - Gudykunst& Kim
Culture, apart
from its primary function of active adaptation to the environment, has another,
derivative, but no less important, function as an exact material and spiritual
environment which mediates and reflects the human collectives and among
them.” -Tokarev
Culture is that complex whole which includes knowledge, belief, art, morals, law, customs, and other capabilities and habits acquired by man as a member of society. -Tylor
Culture is that complex whole which includes knowledge, belief, art, morals, law, customs, and other capabilities and habits acquired by man as a member of society. -Tylor
“Culture is
simply a way of talking about collective identities” – Kuper
Finally,
cultural studies analyze not only the cultural work, but also the means of
production.Political
Economy: “culture includes the organization of production, the structure of the
family, and the structure of institutions which express or govern social
relationships, the characteristic forms through which members of the society
communicate” (Raymond Williams)
Meaning:
“culture is simply the ensemble of stories we tell ourselves about ourselves” - (Clifford
Geertz)
Social
Effects/Interactivity – “culture is the learned behavior of a society or a
subgroup”- (Margaret Mead)
Some Point out
them:-
- Culture as product: “material culture” or “popular culture” versus “high” culture or “folk” culture
- Culture as refinement: moral or intellectual development, human attainment of “perfection”
- Culture as group: the people who share whatever culture is.
I think everyday life is studied in
cultural studies, cultural studies composed of element of Features.
Cultural Studies: Main Concerns
Subjectivity and power relations (Race, gender, class
relations) in culture (cultural hegemony). the circuit of culture
What
is the Subject of Cultural Studies?
•
Subject area not clearly defined; all-inclusive notion of
culture and study of a range of practices.Principles, theories and methods are
eclectic. Distinct history of cultural studies.Principles, theories and methods
from social sciences disciplines, the humanities and the arts adapted to the
purposes of cultural analysis
•
Methodologies diverse: textual analysis, ethnography,
psychoanalysis, survey research, etc.
So than I can Put some images very
good relation on studies in culture and method
Cultural study have 3’cs:
Cultural critics
aim to reveal the political, economic reasons why a certain cultural product is
more baled at certain times than others.
Johnny Depp’s funky performance in
Disney’s Pirates of the Caribbean: The course of the Black Pearl (2003) –
real pirates of the Caribbean such as Blackbeard and Henry Morgan.
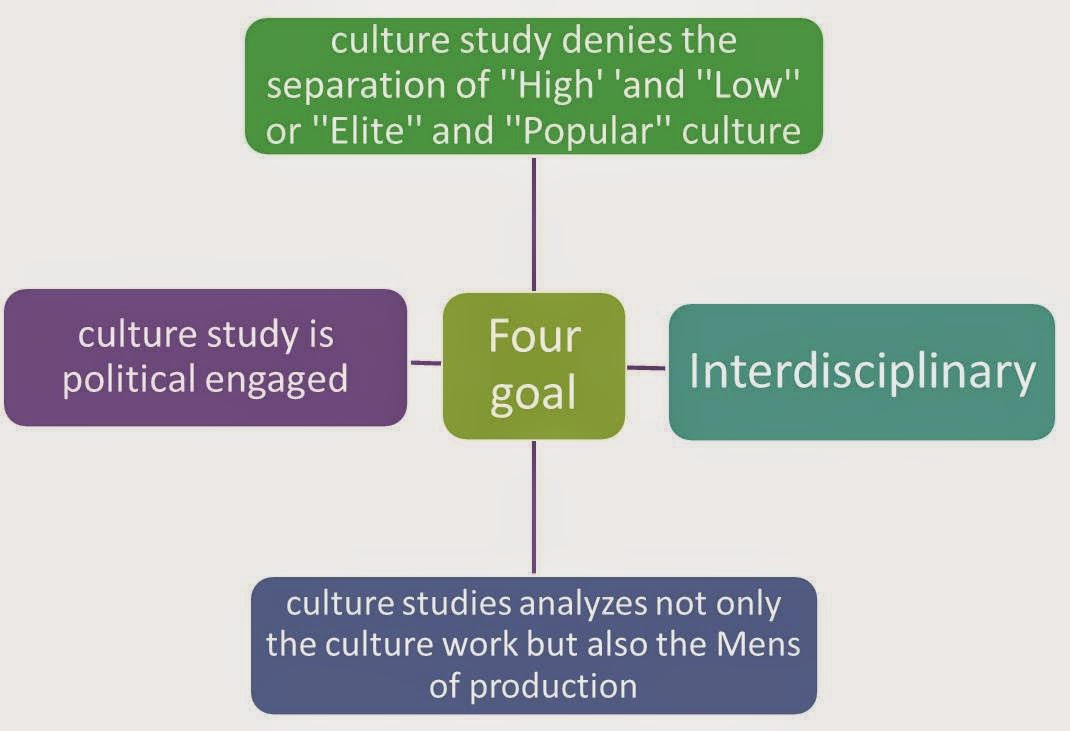
There
are four goals of culture studies as a kind of :
Now let’s our main topic starts here those five
types of culture studies:
When define the culture studies there
are many controversies work are include them and there is most of idea is
related to some power or political relationship between social and capitalism.
(1) British
Cultural Materialism:
Cultural materialism began in earnest in the 1950s
with the work of F. R. Leavis,
heavily influenced by Matthew Arnold’sanalyses of bourgeois culture.
“There are no masses; there are only ways of seeing (other) people as masses.” – Raymond Williams
“There are no masses; there are only ways of seeing (other) people as masses.” – Raymond Williams
Williams talks
about attribute of (1) working class (2) Elite class
It as a four
types of academic literary criticism using in culture perspective as a like:
(1) Aestheticism
(2) Antihistoricism
(3) Formalism
(4) Apoliticis
Feminism was also important for British cultural Materialism .
Cultural materialists also turned to : Insights: Humanistic : Spiritual
Feminism was also important for British cultural Materialism .
Cultural materialists also turned to : Insights: Humanistic : Spiritual
(2) New Historicism:
New histioricism is developed 1980 by Stephan
Greenblatt
Basic
idea: History with literary text
“Text
is historical and history is textual’’ – Michael Warner
History deals with background and text deals with
its foreground so, background and foreground both should be taken into
considerationHistory is a series of an event.According to about History explain to Past sense and Idea about like:
- History is always historicized – Fredrick
- Always historicize and history is that hurt – Fredrick Jamson
- New historicists seek “surprising coincidences” that may cross generic, historical, and cultural lines in borrowings of metaphor, ceremony, or popular culture.
- The new historicism rejects the prioritization of history in favor of ordering history only through the interplay of forms of power.
What does new historicism do?
(1) First
they juxtaposed the post with present
(2) They
deal with the history
(3) It
also deconstruction the text
(4) Derida’s concept
of deconstruction also comes in that.
New Historicism process as :
example:
(1) Rabbit
woman : a female gives birth to rabbit.(it is satire on scientist and female)
(2) Merchant
of Venice: it shows Shakespeare anti-Semitic.
(3)
Laputa – Floating island - The Whore
Here I put image about that idea New Historism is Historisze of history like:
(3) American Multiculturalism:
Turn back the few chapters of
American political history and we witness bloodshed and atrocities in the name
of racism.in this type culture include in four type of writer and many sub
culture activity or interesting about history of American writer. Such a kind
of:
(1)
African American writer :
African American Writing often displays a folkloric
conception of a humankind; a “double consciousness,” as W.E.B. DuBois called
it, arising from bicultural identity; irony, parody, tragedy and bitter comedy
in negotiating this ambivalence; attacks upon presumed white cultural superiority;
a naturalistic focus on survival’ and inventive reframing of language itself,
as in language games liken “jiing,””sounding,””signifying,” and “rapping.”
Langston Hughes was a prominent member of the Harlem Renaissance a movement during the 1920s of black writers and intellectuals who engaged in intense debate regarding the place of the African American in American life, and on the role and identity of the African-American artist.
Langston Hughes was a prominent member of the Harlem Renaissance a movement during the 1920s of black writers and intellectuals who engaged in intense debate regarding the place of the African American in American life, and on the role and identity of the African-American artist.
(2)
Latina/o Writers:
Spanish-speaking
people in the United States. The majority of Mexican residents stayed in place,
transformed into Mexican Americans with a stroke of the pen.One of the primary
tropes in Latina/o studies has to do with the entire concept of borders-borders
between nations, between cultures and within cultures.
“Code-switching” is a border phenomenon studied by linguists.
Speakers who code-switch move back and forth between Spanish and English, for
instance, or resort to the “Spanglish” of border towns.
Liminality,
or “betweeness” is characteristic of postmodern experience but also has special
connotations for Latina/o.
(3)
American Indian Literatures:
Two types of
Indian literature have evolved as fields of study.
(1)
Traditional Indian literature includes tales, songs, and oratory.
(2)
Mainstream Indian literature refers to works written by Indians in English in
the traditional genres of fiction, poetry and autobiography.
Momaday’sHouse
Made of Dawn(1968), which won the Pulitzer Prize, and his memoir, The
way to Rainy Mountain(1969), beginning a renaissance of Indian fiction and
poetry.
In
this type literature another important that :
AIM-
American Indian Movement
ASAL-
Association for the study of American India literature
(4)
Asian American Writers:
¡ Asian
American literature can be said to have begun around the turn of the 20th
century, primarily with autobiographical “paper son” stories and
“confessions.”Edward Said has written of orientalism, or the tendency to
objectify and exoticize Asians, and their work has sought to respond to such
stereotyping.
¡ Paper
son stories were carefully fabricated for Chinese immigrant men to make the
authorities believe that their New World sponsors were really their fathers.
¡ Asian
American autobiography inherited these descriptive strategies, as Maxine Hong
Kingston’s The Woman Warriors: Memoirs of Girlhood Among Ghosts(1976)
illustrates.
¡ Identity
may be individually known within but is not always at home in the outward
community. Most influenced work like:
(4) Popular culture :
It
is also known as POP culture. Of Culture studies also includes mass or popular
cultural and everyday life.
Ø The
department popular culture at Bowling Green Uni. Launched
the journal of popular culture.
Ø Popular
culture is the culture of masses.
There are four
type of popular culture :
(1) Production Analysis: It
ask quotations like:
a) Who
own the media?
b) Who
create text and why?
c) How
democratic of elitist is production of popular culture ?
d) What
about works written only for money?
Example like: Television programme
(2) Textual analysis: It
examines how specific works of popular culture created meanings.
(3) Audience analysis:
it asks different group of popular culture consumers or users, make similar of
different sense of some texts.
(4) Historical analysis: It investigates how these other three
dimensions over times.
(1) Postmodernism & postcolonial
studies
Ø Postmodernism: Postmodernism
questions everything rationalist European philosophy held to be true.Beginning
in the mid-1980s, postmodernism emerged in art, architecture, music, film,
literature, sociology, communications, fashion and other field. Postmodernism
borrows from modernism disillusionment with the givens of society; a penchant
for irony; the self-conscious “play” within the work of art; fragmentation and
ambiguity; and a restructured, decentered, dehumanized subject.
Started
by Ahab Hassan and Lesile Fielder . Earlier this term was known as the culture aesthetics approach.
Post modernism is an anti – art After world war II And they both
have stared and coined this term. ‘Postmodernism’ is a term usually
applied to the period in literature, which was first used in the 1960s. it is a
reaction against realism & modernism.It reject the claim of any
universal or totalizing theory , and reject ‘high’ & ‘low’ class- mass. In literature it collapses the
distinction between genres and conventions.The thriller formats became of
the serious novel. Comic element and absurdity mark
the author’s attitude to tragic, events like death ,suffering. Postmodernism
argues that it is all contingent and that most cultural constructions have
served the function of empowering members of a dominant social group at the
expense of “others.”
Practitioners- modernism:
a) Walter
Benjamin
b) Susan
Sintag
c) Loui’s
Borges
d) Virginia
wolf
e) Martin
Heidegger
f) BertoltBrtech
g) Ezrapound
h) Jams
joyee
v
Postmodernism Aspect by Jean
Baudrillard some point out that:
ü Any
sign is empty
ü Virtual
world
ü Status
and taboos
ü Hyperrealism
between the private or public.
It also
affected in
-
Building - Cinema
-
Literature - music
-
Painting - Architecture
-
Photography
Ø
Postcolonial
Studies :
¡ Post
colonialism refers to a historical phase undergone by the Third World countries
after the decline of colonialism.
¡ “others”
constructs them based upon Western anxieties and preoccupations. Said
sharply critiques the Western images of the Oriental as “irrational, depraved
(fallen), child-like, ‘different,’” which has allowed the West to define itself
as “rational, virtuous, mature, ‘normal.’”
¡ Post
modern intellectual discourse.
¡ The
association between nations and area they occupied and once ruled.
Many
Third World writers focus on both colonialism and the changes created in a
postcolonial culture.Frantz Fanon drew upon his own horrific experiences in
French Algeria to deconstruct emerging national regimes.
¡ Homi
K. Bhabha’s
postcolonial theory involves analysis of nationality, ethnicity, and
politics with poststructuralist ideas of identity and indeterminacy, defining
postcolonial identities as shifting, hybrid construction.
¡ Among
postcolonial feminism is Gayatri Chakravorty Spivak, who
examines the effects of political independence upon “subaltern” or subproletarian
women in the Third World.
¡ Reveal
how female subjects are silenced by the dialogue between the male-dominated
West and East, offering little hope for the subaltern woman’s voice to rise up
amidst the global social institutions that oppress her.
In their Homi K.
Bhabha critical worked that idea founder
of as a real or clonal idea. He was analyzed postcolonial theory like:
Ø Postcolonial Theorist ;
i.
Rudyard Kipling
ii.
E.M. Foster
iii.
Jamaica Kincaid
iv.
Jean Rhys
To wind up:
In their last
conclude that five type culture is very longer theory or many sub divisor or
theorist become to his research and include to culture as a subjectivity own
work.